Braces are a common orthodontic treatment used to straighten teeth, correct bite issues, and improve overall oral health. However, wearing braces requires extra attention to oral hygiene to prevent complications such as cavities, gum disease, and staining. This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to care for your mouth while wearing braces, ensuring a healthy smile during and after your orthodontic treatment.
The Importance of Oral Hygiene with Braces
Braces create additional nooks and crannies where food particles and plaque can accumulate, making it more challenging to maintain oral hygiene. Neglecting oral care while wearing braces can lead to:
Tooth Decay:
Plaque buildup around braces can cause cavities.
Gum Disease:
Inflammation and infection of the gums can occur if plaque is not effectively removed.
Staining:
Braces can cause uneven staining if plaque is not regularly removed.
Bad Breath:
Accumulated food particles and plaque can lead to persistent bad breath.
Daily Oral Care Routine
1. Brushing
Brushing with braces requires a bit more effort and time to ensure all surfaces are clean.
Frequency:
Brush your teeth at least twice a day, preferably after every meal.
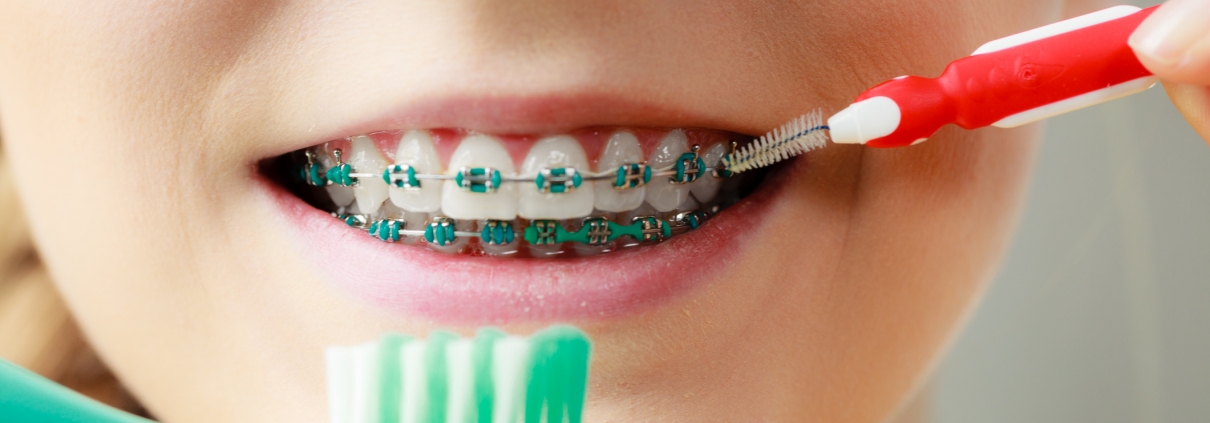
Tools: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush or an electric toothbrush. An interdental toothbrush, also known as a proxy brush, can help clean around brackets and wires.
Technique:
Start by brushing at a 45-degree angle to the gums.
Brush the top of the brackets by angling the brush down.
Brush the bottom of the brackets by angling the brush up.
Ensure you brush the chewing surfaces, the backs of the teeth, and the gumline.
2. Flossing
Flossing with braces can be challenging but is essential to remove food particles and plaque between teeth.
Tools: Use floss threaders or orthodontic flossers designed to work around braces.
Technique:
Thread the floss under the main wire.
Carefully floss between the teeth, moving up and down along the sides of each tooth.
Be gentle to avoid damaging the wires and brackets.
3. Mouthwash
Using an antimicrobial or fluoride mouthwash can help reduce plaque and strengthen tooth enamel.
Frequency:
Rinse once daily, ideally before bed.
Benefits:
Mouthwash can help reach areas that brushing and flossing might miss, providing an extra layer of protection against cavities and gum disease.
Additional Tips for Oral Care with Braces
1. Avoid Certain Foods
Some foods can damage braces or increase the risk of tooth decay.
Sticky and Chewy Foods:
Avoid caramel, gum, and other sticky candies that can get stuck in braces.
Hard Foods:
Nuts, hard candies, and ice can break wires and brackets.
Sugary Foods and Drinks:
Limit sugary snacks and beverages that can lead to plaque buildup and cavities.
2. Regular Dental Check-ups
Continue to visit your dentist and orthodontist regularly for professional cleanings and check-ups.
Frequency:
Schedule dental cleanings every six months and follow your orthodontist’s recommended appointment schedule.
Professional Cleanings:
Professional cleanings can remove plaque and tartar that regular brushing and flossing might miss, reducing the risk of cavities and gum disease.
3. Use Orthodontic Wax
Orthodontic wax can provide relief from irritation caused by braces.
Application:
Apply a small piece of wax to the brackets or wires that are causing discomfort.
Removal:
Remove the wax before brushing your teeth.
4. Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water helps wash away food particles and bacteria, maintaining a clean mouth.
Rinsing:
Rinse your mouth with water after eating if you can’t brush right away.
Hydration:
Staying hydrated also helps prevent dry mouth, which can increase the risk of cavities and gum disease.
Managing Common Issues with Braces
1. Soreness and Discomfort
It’s common to experience soreness when braces are first applied or adjusted.
Pain Relief:
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help manage discomfort.
Soft Foods:
Eat soft foods such as yogurt, mashed potatoes, and smoothies until the soreness subsides.
2. Broken Brackets or Wires
Broken brackets or wires can cause discomfort and need to be addressed promptly.
Temporary Fixes:
Use orthodontic wax to cover the broken part and prevent irritation.
Contact Your Orthodontist:
Schedule an appointment to repair the broken bracket or wire as soon as possible.
3. Plaque and Tartar Buildup
Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial to preventing plaque and tartar buildup.
Interdental Brushes:
Use interdental brushes to clean between brackets and under wires.
Fluoride Treatments:
Ask your dentist about fluoride treatments to help strengthen enamel and prevent decay.
Conclusion
Caring for your mouth while wearing braces requires extra effort and attention, but the results are well worth it. By following a diligent oral hygiene routine, avoiding damaging foods, and seeking regular professional care, you can ensure your teeth and gums remain healthy throughout your orthodontic treatment. These practices will help you achieve a beautiful, healthy smile once your braces are removed, contributing to your overall well-being and confidence.