Root canal
Previously, a tooth whose root had become infected had to be extracted. However, in 95% of cases today, this is no longer the case. Root canal therapy treats the root (also called the pulp) of the tooth. Today, in new dental technology, wisdom tooth denervation has become a relatively painless technique that allows you to preserve your teeth instead of losing them. Widespread tooth decay, trauma, tooth fracture, and gum disease can cause tooth loss and can cause symptoms, such as pain when chewing and pressing on the tooth, tooth sensitivity to cold and heat that lasts longer than usual. Whatever the cause of the nerve canal problem, your teeth can be saved by using root canal therapy.
What is root canal therapy?
In Greek, “endo” means inside and “dent” means tooth, so endodontic treatment means healing the space inside the tooth. Knowing the anatomy of the tooth will help to understand the root canal treatment. Inside the tooth, beneath the white enamel and hard layer called dentin, is the soft tissue of the tooth root. The root of the tooth contains blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissues, and as the tooth grows, it forms the hard tissue that surrounds the tooth. Root tissue extends from the crown of the tooth to the tip of the tooth root, where it attaches to the surrounding tissue of the tooth root. Root tissue plays an important role in tooth growth. However, after full growth, the tooth can remain without roots, because the tooth can feed on the surrounding tissue.
How does root canal therapy protect teeth?
Root canal therapy removes inflamed and infected tissue from the root and thoroughly cleans and shapes the root canal, then fills and closes the empty space in the root canal. You can then see your dentist again for a veneer or other restorative treatment to fully restore tooth function. After restoration, the denervated tooth acts like any of your other teeth.
Why may a tooth need root canal therapy?
Root canal therapy becomes necessary when the root (soft tissue inside the root canal) becomes inflamed or infected. Inflammation and infection of root tissue can occur for a variety of reasons:
Tooth Decay
Perform repeated treatments on the teeth
There are cracks or fractures in the teeth
Any blow to the tooth, even if it does not cause a fracture or apparent crack on the tooth, can lead to damage to the root tissue of the tooth. If inflammation or infection of the root tissue is not treated, it can lead to toothache and eventually tooth abscess.
Signs that the tooth needs root canal therapy:
Symptoms to look out for are:
Pain
Prolonged sensitivity to heat and cold
Sensitivity to touch and chewing
Jaundice and tooth staining
Swelling
Sensitivity and fluid leakage from abscess sacs and adjacent bone and gum tissue
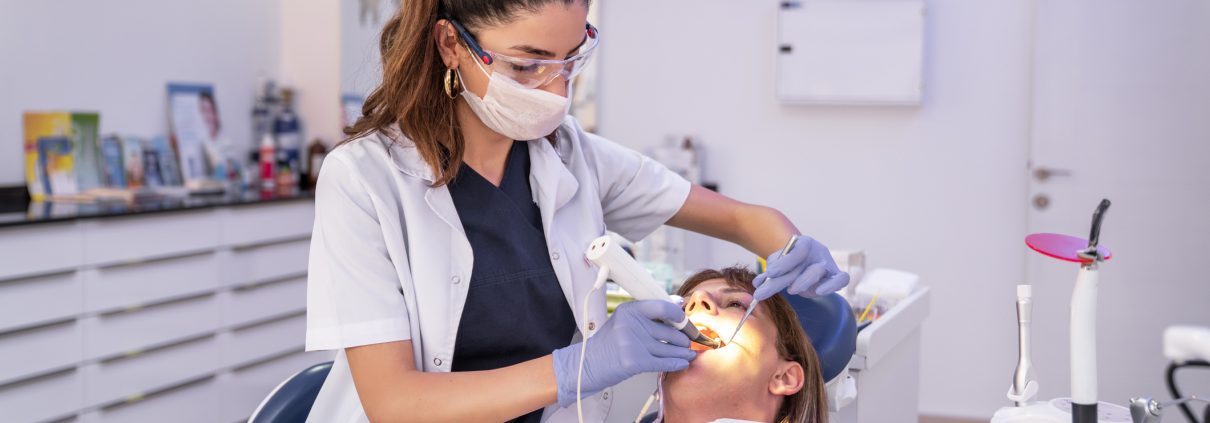
How to perform root canal surgery
Root canal therapy is often performed in one or two visits to the dentist and includes the following steps:
The root canal specialist injects local anesthesia after examining the tooth and examining the photo taken of the tooth. After the tooth is anesthetized, he places a small protective layer of rubber to keep the tooth dry in that area to separate the tooth from adjacent teeth and prevent saliva from entering it.
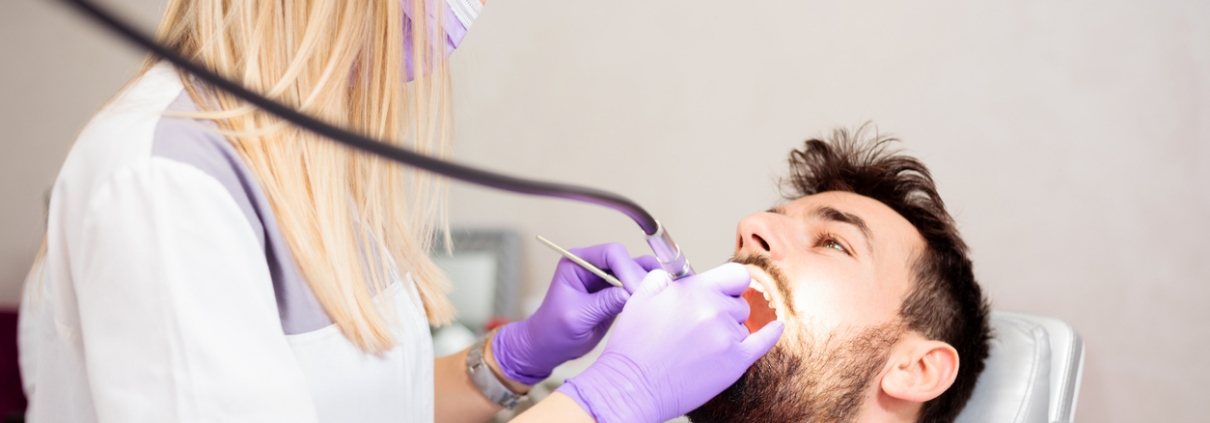
The orthodontist then pierces the crown and uses very fine tools to remove the root tissue from the root canal and root canals and to shave the root canal and fill it with dental fillings.
After the root canal is cleaned and shaved, the root canal specialist fills the space inside the root with environmentally friendly fillers (usually a rubber-shaped material called rubber). In order to completely seal the root space, this filler is placed inside the root space with adhesives. In some cases, a temporary filler is placed on the root canal to close the entrance. Before the tooth is restored, this temporary filling material is removed by the dentist.
After the final referral to a root canal specialist, you should see a dentist to place a veneer or other restorative material on the tooth and protect and restore it to its full function.
If the tooth does not have the proper structure to hold the restorative material inside, the dentist or endodontist may place an abutment inside the tooth. You can get more details about different methods of repairing your teeth by asking your dentist.
Will you feel any pain during the denervation treatment?
Many root canal procedures are performed to relieve toothache caused by inflammation or infection of the root. With new techniques and local anesthesia applied, most patients do not feel any pain during endodontic treatment.
Your teeth may be sensitive for the first few days after treatment, especially if you had a toothache before the neurosurgery treatment. This allergy can be treated with over-the-counter medications or prescribed by your dentist. Follow the instructions of your root canal specialist completely. For some time after the denervation, your tooth will look slightly different from other teeth. However, if you feel severe pain or pressure that lasts for more than a few days, be sure to contact your endodontist.