Losing teeth makes you look older! Today, we live in a society that is looking for ways to reverse the signs of premature aging. We avoid the sun, we use different facial moisturizers, and we pay attention to our nutrition to reduce wrinkles. But did you know that your missing teeth can also cause signs of aging? Aging due to tooth loss can increase wrinkles on your face.
You know that replacing missing teeth creates a more beautiful smile. However, you may not know that losing teeth can drastically change the shape of your face.
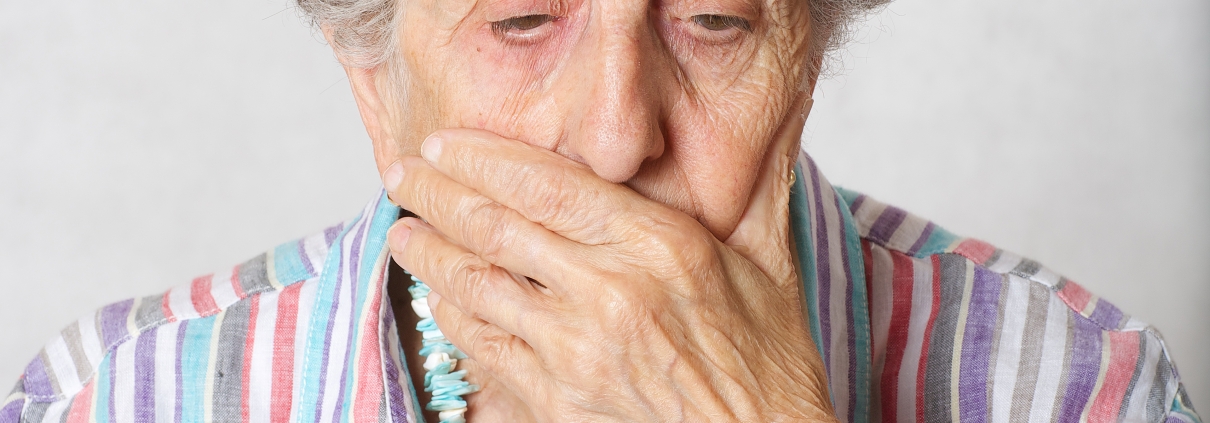
In healthy mouths without tooth loss, the roots of the teeth are supported by the jawbone. When the teeth are lost, the jawbone gradually shrinks and as a result the support of the face is reduced. In other words, with the loss of each tooth, the support of the bones and muscles of the face is lost, which can change your appearance. Without teeth for support, facial sagging such as hollows and sagging cheeks can appear and make you look older than you really are.
The importance of replacing missing teeth
In addition to supporting the facial profile, teeth help improve chewing, digestion, speech, and even self-confidence. Studies have shown that tooth loss can have a negative effect on self-esteem.
Since we know that teeth keep the muscles and bones of your face intact, we can say that there is a relationship between missing teeth and early signs of aging. Without the support provided by your teeth, your mouth and cheeks can droop, contract, and droop, often referred to as a sagging cheek.
While some dental gaps may seem insignificant, they allow existing teeth to move, which also affects facial support. So, even if you only lose a few back teeth, those teeth can shift and cause a domino effect that can also change the position of your front teeth. Gaps in front teeth can negatively affect your appearance.
Unfortunately, an aging face is not the only problem with tooth loss. Tooth loss also causes lifestyle changes. Without full dental support, people have difficulty chewing, speaking or smiling. Tooth loss can become a major obstacle to any additional tooth loss and not just an inconvenience.
Aging due to tooth loss
Facial aging is a lesser known problem that people think about when they lose their teeth. Symptoms of premature aging caused by tooth loss include the following facial profile changes.
Facial Angles: When you lose teeth, you also lose jawbone height, which lowers the height of your face. Changing the angle can change the shape of the face and make the nose look bigger. Losing the normal shape of the face makes the face look hollow.
Facial Wrinkles: Changes in the angle of the face can increase vertical lines that make you look older than you really are.
Bite Changes: Tooth loss causes changes in the way the teeth bite together. Deviations in bite can create a tighter appearance as the corners of your mouth lose their shape.
Frowning and sad appearance: Losing the shape of the corners of the mouth can unintentionally make you look sad or even angry.
When part of the jawbone is lost, it weakens the muscle ligaments, which causes the facial tissue to sag.
Thin lips: Lips can look thin without teeth to support a fuller lip appearance. In addition, the weakening of the muscles around the mouth with the loss of teeth can make fuller lips appear longer and older.